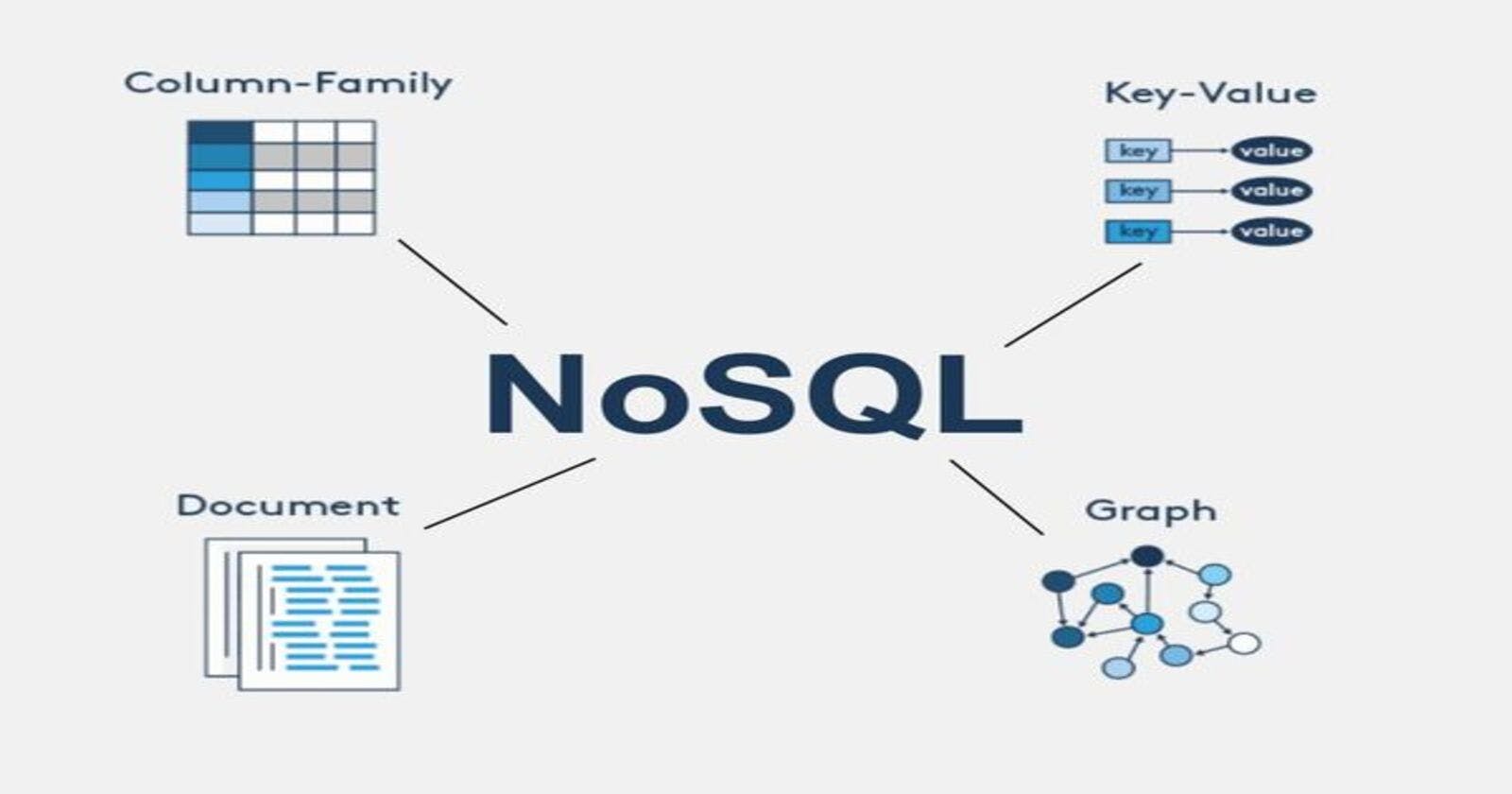
NoSQL databases have been all the rage in the 21st century, and with good reason. They are fast, easily scalable, don't require a schema, and in general, are more flexible than their SQL counterparts.
Here's a brief overview of the types of NoSQL databases, and where they can be used-
Key-Value stores- As the name suggests, the data is stored in the form of keys and values.
Keys can be thought of as identifiers; like people have names, values have keys to distinguish them.
These databases are used when the data being stored isn't very complex.
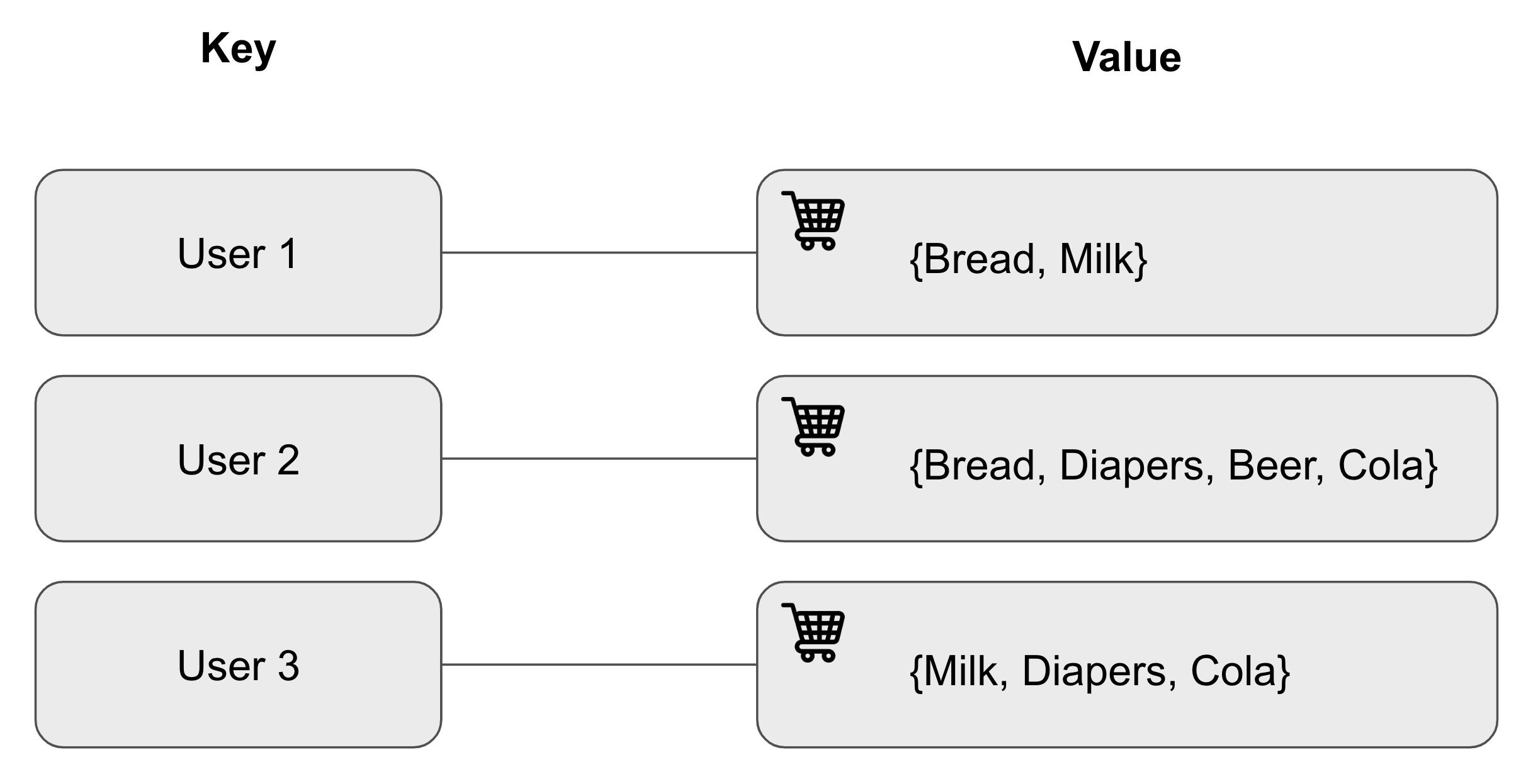
For example, products(values) in a shopping cart can be mapped to a user(key).
Some popular key-value databases are Amazon DynamoDB, CouchBase, Aerospike, Riak and Berkeley DB.
Document stores- They are used to store and query data in the form of JSON or other similar formats.
All the records are stored in a single document, without having to create a schema.
Multiple documents grouped together are called collections, and the database can consist of several such collections.

They are commonly used for web-based applications such as blogging websites, where each user can contain multiple blogs in the form of a list.
Some popular document store databases are MongoDB and CosmosDB.
Wide-column stores- Wide-column stores are used to store data in the form of flexible columns instead of storing them as rows.
This form of columnar storage makes data retrieval fast and reduces querying time.
However, it should be noted that you shouldn't perform join operations on them and you shouldn't use them for ad hoc query patterns, high-level aggregations and when the requirements of the database change frequently.
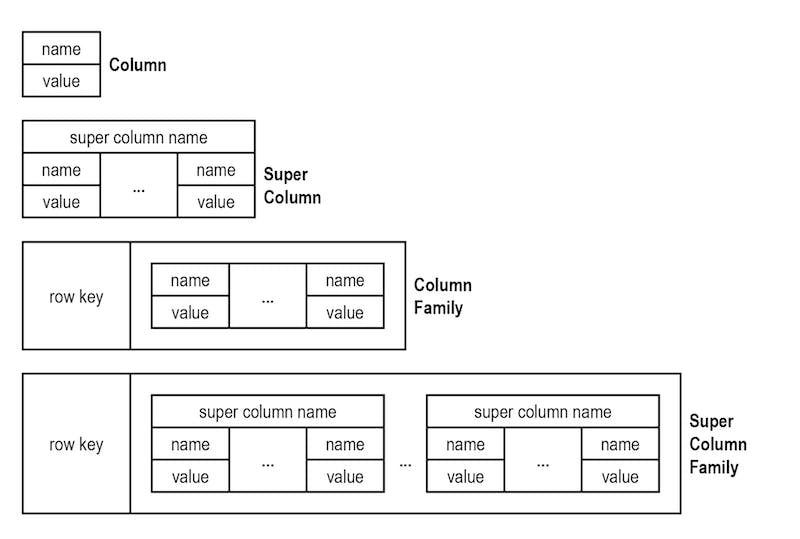
As seen in the figure, a single attribute-value table is called a column, multiple columns are called a super column, a single super column associated with a row key is called a column family, and multiple super columns associated with a row key are called a super column family.
They are used to store time series data, real-time data analytics and trading data.
Some popular wide-column store databases are Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase, ScyllaDB and Google BigTable.
Graph databases- Again, the name describes the essence of these databases, which are stored as graphs that contain nodes and edges.
The nodes represent entities of the database and the edges represent the relationships between these entities.
Furthermore, each node can contain a set of properties that give more details about that particular entity.
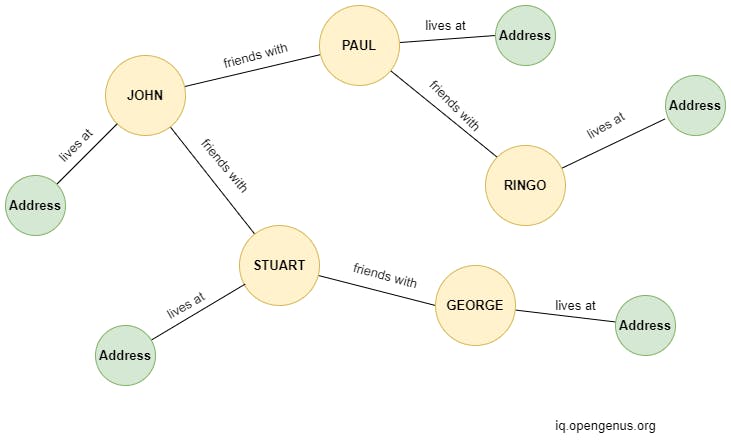
The most common use cases for graph databases are in, you guessed it, social networking sites. They can also be used in recommendation engines and fraud detection mechanisms where trails of transactions between multiple accounts are monitored.
Some popular graph databases are Neo4j, ArangoDB, Apache Giraph and Amazon Neptune.
Search engine databases- These databases are used to search data either via a web search or a full-text search.
They use an index to categorize data records that have similar characteristics.
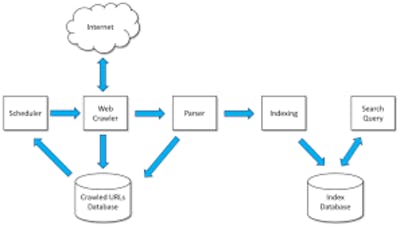
Some common use cases are for providing auto-complete/auto-suggestion features, log analysis in software applications and time-series data.
Elasticsearch and Apache Solr are examples of search engine databases.
If you found this helpful, consider liking and sharing it, and subscribing to my newsletter. Feel free to leave your thoughts, questions and ponderings in the comments.
You can also follow me for more data and ML-related content. I focus on demystifying technical jargon and encouraging newcomers in the field by explaining concepts as simply as possible.
This is Sachin being succinct :)